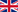
The country can be divided relatively into the climatic zones as follows:
1/The Northeast (Ha Giang, Cao Bang, Bac Kan, Lang Son, Quang Ninh, Tuyen Quang, Thai Nguyen, Bac Giang, Bac Ninh, Hanoi, Hai Duong, Hung Yen, Hai Phong, Ha Nam, Nam Dinh, Ninh Binh).
2/The Northwest (Lao Cai, Lai Chau, Dien Bien, Son La, Yen Bai, Hoa Binh, Vinh Phuc, Phu Tho).
3/North of the Central Region (Thanh Hoa, Nghe An, Ha Tinh).
4/The middle of the Central Region, north of the Hai Van Pass (Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Hue).
5/The south of the Central Region (Da Nang, Quang Nam, Quang Ngai, Binh Dinh, Phu Yen, Khanh Hoa, Ninh Thuan).
6/The Central Highlands (Kon Tum, Gia Lai, Dak Lak, Dak Nong, Lam Dong)
7/The South of Vietnam (including all the provinces in the Mekong Delta, along the coast and south of the Central Highlands).
The Monsoons in Vietnam and the Influence of the Topographical Relief to Vietnam’s regional climates
During the winter, from November to April, the air masses in the northern hemisphere are not heated as much as those around equator and in the southern hemisphere. The air masses are warmer at sea than further in the continent. The monsoon forms blowing from Siberia through China and Mongolia, from north to south and seawards. In Vietnam, this is called the Northeasterly Monsoon which causes the winter in northern Vietnam and the north of the Central Region of Vietnam. The cold monsoon also forms originating from the cold air masses in northern China but this causes only mild cold temperatures in northern Vietnam at the beginning and at the end of the winter.
The winter monsoon reaches Vietnam via two ways: Chinese continent and through the Sea of Japan, East China Sea, and East Vietnam Sea. The later can cause rains in northern Vietnam.
Thanks to the Hoang Lien Mountain Range which runs from the northwest to the southeast which blocks the monsoon that makes the eastern side (which is the Northeast of Vietnam) more humid and colder than the western side (the Northwest of Vietnam). There are several high mountains in the Northeast of Vietnam but these mountains mostly run from east to west which facilitates the winter monsoon rather than blocks it. The winter tends to last longer in the Northeast than in the Northwest of Vietnam.
The middle of the Central Region of Vietnam is bounded by the low-altitude coastal area, the high Hoanh Son Mountain to the north, the high Truong Son Mountain Range to the west and the high Hai Van – Bach Ma Mountain Range to the south. These mountains help accumulate moisture in the middle of the Central Region. Also, the winter monsoon tends to be less cold and more humid as it goes from north to south. As a result, the middle of the Central Region of Vietnam has a mild winter accompanied by lot of prolonged rains.
The Hai Van – Bach Ma Mountain Range, which runs east-west blocks most of the winter monsoon, which makes the temperatures in the south Central Coast of Vietnam not as low as those to the north. But because of the Truong Son Mountain Range which runs on the west of this region (in fact the full length of the Central Region) that blocks the monsoon that it often receives rains during the time of the winter monsoon.

The low-land region of northern Vietnam has a tropical monsoon climate with 4 seasons per year. The highest temperature in the summer may reach above 40 Degrees Celsius and the lowest temperature in the winter may reach 5-6 Degrees Celsius.

The low-land area along the coast in the Central Region of Vietnam is constantly hit by waves of heat in the summer which is made worse by the dry and hot monsoons from Laos. The temperature may reach up to 43-45 Degrees Celsius in the summer and there's always lack of water.
Also, the region is the destination of the worst typhoons coming to Vietnam which cause disastrous floods and landslides in the months of September, October and November.
In the summer months (April-September), Vietnam receives 2 main monsoons: The Southwesterly Monsoon and the Southeasterly Monsoon. The Southwesterly Monsoon is formed because the air masses are heated more in the northern hemisphere than in the southern hemisphere and the air masses in the continents are heated more than those on the oceans.
The Southwesterly Monsoon in Vietnam originates from the high pressure air of the equator and that of the north of the Indian Ocean. This monsoon is moist and pleasant in South Vietnam. But when reaching the Central Region and the North of Vietnam, it is very hot and dry. The reasons for which could be partially attributed to the high mountains to the western side of the country which accumulates the moisture on the western side of the mountains making the air blowing over it dry. Another reason is the hot temperatures in Thailand and Laos which the monsoon travels through.
The regions in Vietnam strongly influenced by the Southwesterly Monsoon are in the Central Region and South of Vietnam. In the North of Vietnam, the provinces strongly influenced by the Southwesterly are Dien Bien, Lai Chau, Hoa Binh, Son La. The Southwesterly Monsoon causes daily short-lived rains in South of Vietnam and the Central Highlands; in the other regions of Vietnam, it causes hot and dry summer.
Formed in the same way, the Southeasterly Monsoon, occurring from May to October, the heated air of the Gobi Desert rises, far to the north, inducing moist air to flow inland from the sea and depositing heavy rainfall. Due to the topographical relief of the Central Region of Vietnam, the rains are prolonged and heavy. The Southwesterly Monsoon is hot and dry in the North and Central Region of Vietnam, the Souththeasterly Monsoon is moist and pleasant.
As the Earth moves around the Sun, the much heated air changes from one place to another and the monsoons in Vietnam change accordingly. While typhoons hit northern Vietnam in the summer from June to October, they hit the Central and South Vietnam a bit later from August to November. Late in the summer and during autumn in northern Vietnam, the cool air to the north tends to push southwards all possible typhoons, which forms to the east of the East Sea of Vietnam.
Rains in Vietnam
Annual rainfall is substantial in all regions and torrential in some, ranging from 1,200-3,000mm. The average annual rainfall is about 1,500-2,000mm. In the North of Vietnam, most precipitation occurs in the summer (June-October). In the Central Region of Vietnam, most rainfall is from August through November. In the Central Highlands and South Vietnam, most rainfall is from May through October.
The temperatures in Vietnam
Temperatures in Vietnam range from below freezing point (in December-February, the coolest months) to more than 38°C (in May-July, the hottest months). The mountainous region to the far-north of Vietnam and the Central Highlands have the lowest temperatures. The middle and north of the Central Regions have the highest temperatures (in June-July). The South of Vietnam is hottest in April and early May.
Seasons in Vietnam
Seasonal divisions are more pronounced in the North than in the Central Region and in the South of Vietnam. In the South of Vietnam, seasonal temperatures vary only a few degrees usually in the 25°C-33°C range.
In the North, the summer, which is also the rainy season, prevails from May to mid August. The average temperature in Ha Noi is about 33°C during this period, with very high humidity.
From September through November, it's supposed to be Autumn in the North. While it is normally perfectly nice, dry and breezy weather, sometimes it is to stormy and rainy for a couple of days. The average temperature during this time is 25°C-28°C.
During the winter in the North of Vietnam from December to March, the average temperature is 15°C. It is mostly dry, there could be light drizzles sometimes.
The North of Vietnam, with the exception of Son La & Dien Bien, experiences a lovely spring from late March to early May. While during this time, Son La and Dien Bien enjoys very warm summer with strong warm and dry westerly winds (foehn monsoon).

Sapa, a hill station in the North West of Vietnam with the elevation of over 1,500 m above sea level has a temperate climate with average temperatures ranging from 15 to 25 Degree Celsius. A sunny as per the photo is a real treat for the local H'Mong People of Sapa.

Like Sapa, Dong Van Rock Plateau of Ha Giang in the far-north of Vietnam with the elevation above 1,000 above sea level has a temperate climate. While Sapa's weather tends to be moist and cold, Dong Van of Ha Giang tends to be cool, dry and fresh.

Moc Chau Plateau of Son La Province in northern Vietnam has the average elevation of 1050m above sea level. Moc Chau has a temperate climate with temperatures ranging from 18-25 Degrees Celsius.

Da Lat with the elevation of 1475m, hidden deep in the Lang Biang Plateau, has a temperate climate and dubbed "The City of Eternal Spring". The average temperature of Da Lat is 18-21 Degrees Celsius.
The rainy season in the Central Region of the country (Hue, Da Nang, Hoi An, Nha Trang...) lasts from September to February. Whenever it rains, things are gloomy and cool in Hue, Hoi An and Da Nang. From February through April, it's pleasant without rains and with breezy weather. From May to July it is dry and hot, the temperatures may get up to 36°-40°C around this area.

The old town of Hoi An in Quang Nam Province (central region of Vietnam) could look much "older" in the rain
In the South, Ho Chi Minh City and the Mekong Delta experience a year-round hot and humid tropical climate with daily temperatures normally between 28°C-33°C. The hottest time is March & April to early May during which the temperatures are normally above 35°C. The rainy season lasts from May to November, with heavy rains for 30 minutes every day which refresh the atmosphere of oppressive heat. The South of Vietnam has the best weather without rains and with pleasant temperatures (20-30°C) from November through February.

The threatening dark cloud ushering in the rain which would last mostly for less than an hour (Photo at Ben Tre Vietnam)

Rain at U Minh Thuong National Park - Kien Giang Province
What is the best time to visit Vietnam?
To sum up, Vietnam is a country of different weather patterns and climates. Traveling through Vietnam at anytime of the year, you’ll get lovely sunshine here and not too pleasant weather there. If you do not want rains on your holidays, then you may like to consider visiting Vietnam in March-May during which it is the warmest temperatures in the South of Vietnam.
The most beautiful moments in the North of Vietnam are found in Autumn (August-October) but sometimes it rains a couple of days due to typhoons. Another nice period in the North of Vietnam is during March-April.
The Central Region of Vietnam experiences the best weather from mid January through February with pleasant temperatures and without endless rains. Else, you’ll get either oppressive heat or prolonged rains.
The South of Vietnam enjoys the best weather in November through February: pleasant temperatures and without rains.
Another factor you may want to know is that the beautiful weather time in Vietnam is also the busy tourist season. Be prepared for a bigger budget for your Vietnam vacation, crowded restaurants and busy tourist attractions, and overbooked flights and trains. Make a tour to Vietnam in the not so beautiful weather period, you'll get some rains and some sunshine anyway; but things are cheaper and you'll enjoy the whole country to yourself! So, why not keep it positive and enjoy going with the flow; you’ll certainly have a wonderful trip in Vietnam!